11387. Cards game
Huseyn and Yaroslav are playing a card
game. There are n cards laid out in a row on
the table, each with a different number written on it. The players take turns. Huseyn starts the game. On
each turn, a player can take either the leftmost or the rightmost card. The
player will always choose the card with the highest number. The game ends when
there are no cards left on the table.
Input. The first line contains the number of cards n (1
≤ n ≤ 10000) on the table. The second line contains n
positive integers, each indicating the number on a card. All numbers are not
greater than 109.
Output. Print the sum of the numbers on the cards collected by
Huseyn and Yaroslav at the end of the game.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
7 4 7 5 1 12 8 2 |
18 21 |
SOLUTION
two pointers
Algorithm analysis
Let the
array m contain the numbers written on the cards. We initialize pointers
i = 0 at the beginning of the array and j = n – 1 at the end of the array.
On each turn, a player takes
the card with the maximum value max (m[i], m[j]), after which the card is
removed from the table (perform the operation i++ if the card m[i] is chosen, and j-- if the card m[j] is chosen). For each
player, we keep track of the sum of the selected cards in two variables. The
process continues until all cards are removed from the table, that is, until
the pointers i and j
meet.
Example
The game will proceed as
follows.
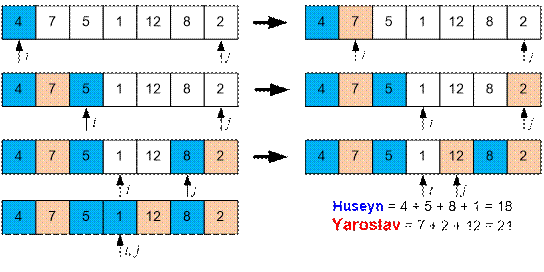
Algorithm realization
Declare
the arrays. The sum of the numbers on the cards collected by Huseyn and
Yaroslav will be stored in res[0] and res[1], respectively.
int m[10001], res[2];
Read
the input data.
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &m[i]);
Set the pointers i = 0 and j = n – 1.
i = 0; j = n - 1;
The players take turns, making n moves in total. Huseyn
takes turns for even k, and Yaroslav takes turns for odd k.
Accordingly, Huseyn’s sum will accumulate in res[0], and Yaroslav’s sum will
accumulate in res[1].
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
On each turn, the player chooses the card with the maximum
value max(m[i], m[j]).
if (m[i] > m[j])
res[k % 2] += m[i++];
else
res[k % 2] += m[j--]; ;
}
Print
the answer.
printf("%d %d\n", res[0], res[1]);
Python realization
Read
the input data.
n = int(input())
m = list(map(int, input().split()))
Set the pointers i = 0 and j = n – 1.
i, j = 0, n – 1
The
sum of the numbers on the cards collected by Huseyn and Yaroslav will be stored
in res[0] and res[1], respectively.
res = [0, 0]
The players take turns, making n moves in total. Huseyn
takes turns for even k, and Yaroslav takes turns for odd k.
Accordingly, Huseyn’s sum will accumulate in res[0], and Yaroslav’s sum will
accumulate in res[1].
for k in range(n):
On each turn, the player chooses the card with the maximum
value max(m[i], m[j]).
if m[i] > m[j]:
res[k % 2] += m[i]
i += 1
else:
res[k % 2] += m[j]
j -= 1
Print
the answer.
print(res[0], res[1])